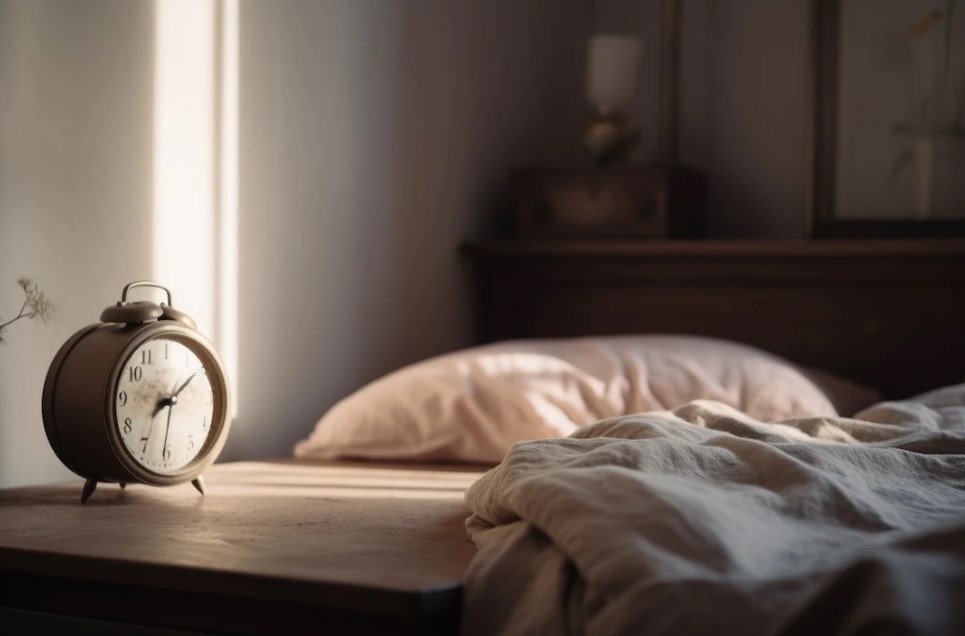
In a fast-paced world filled with constant stimulation, achieving quality sleep has become a challenge for many. The term “sleep hygiene” refers to a set of practices and habits that promote consistently good sleep. Let’s delve into essential sleep hygiene tips to help you unlock the secrets to a restful night’s sleep.
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene involves adopting behaviors and environmental factors that contribute to better sleep quality.
B. Importance of Good Sleep
Quality sleep is vital for physical health, mental well-being, and overall daily functioning.
C. Common Sleep Issues
Understanding common sleep problems helps in implementing effective sleep hygiene practices.
II. Establishing a Sleep Routine
A. Consistent Sleep Schedule
Maintaining a regular sleep pattern helps regulate the body’s internal clock.
B. Bedtime Rituals
Incorporating relaxing pre-sleep rituals signals the body that it’s time to wind down.
C. Creating a Comfortable Sleep Environment
Optimal room conditions, including darkness and comfortable bedding, contribute to a conducive sleep environment.
III. Digital Detox Before Bed
A. Impact of Screens on Sleep
The blue light emitted by screens interferes with the production of the sleep hormone melatonin.
B. Limiting Screen Time
Reducing screen exposure an hour before bedtime aids in better sleep initiation.
C. Blue Light Filters
Using blue light filters on devices helps mitigate the sleep-disrupting effects of screens.
IV. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
A. Importance of Relaxation
Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation, promotes a calm state before bedtime.
B. Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises assist in reducing stress and calming the nervous system.
C. Meditation for Better Sleep
Practicing mindfulness meditation enhances sleep quality and duration.
V. Physical Activity and Sleep
A. Exercise’s Role in Sleep
Regular physical activity promotes deeper and more restorative sleep.
B. Timing of Exercise
Exercising earlier in the day is more beneficial for sleep than vigorous activity close to bedtime.
C. Suitable Activities for Better Sleep
Low-intensity activities, like yoga, are conducive to relaxation and improved sleep.
VI. Dietary Habits
A. Impact of Diet on Sleep
Avoiding heavy meals close to bedtime prevents discomfort and indigestion.
B. Foods to Avoid Before Bed
Limiting caffeine and sugar intake before sleep helps in achieving quality rest.
C. Sleep-Inducing Foods
Incorporating sleep-friendly foods, such as almonds and kiwi, can aid in promoting better sleep.
VII. Managing Stress and Anxiety
A. Recognizing Stressors
Identifying and addressing sources of stress contributes to better sleep.
B. Stress Reduction Techniques
Engaging in stress-relieving activities, like journaling or taking a warm bath, promotes relaxation.
C. Professional Help for Chronic Stress
Seeking professional guidance for chronic stress ensures comprehensive support.
VIII. Sleep Aids and Supplements
A. Caution with Sleep Medications
Consulting with a healthcare professional before using sleep medications is crucial to avoid potential side effects.
B. Natural Sleep Supplements
Certain supplements, like melatonin, can aid in regulating sleep-wake cycles.
C. Consultation with a Healthcare Professional
Seeking medical advice ensures personalized recommendations for sleep aids.
IX. Power of Power Naps
A. Benefits of Short Naps
Short naps can enhance alertness and performance.
B. Ideal Nap Duration
Napping for 20-30 minutes prevents grogginess and supports productivity.
C. Best Times for Power Naps
Choosing optimal times for napping, such as early afternoon, aligns with natural energy fluctuations.
X. Consistency is Key
A. The Importance of Regularity
Consistency in sleep hygiene practices establishes a stable sleep routine.
B. Adapting Sleep Hygiene Habits
Adjusting habits to fit personal preferences and lifestyle ensures sustainable changes.
C. Monitoring and Adjusting as Needed
Regularly evaluating sleep hygiene practices allows for necessary adjustments to optimize results.
XI. Common Sleep Myths
A. Debunking Sleep Myths
Dispelling common misconceptions about sleep aids in making informed choices.
B. Understanding Sleep Facts
Separating fact from fiction contributes to better sleep hygiene decisions.
C. The Truth About Sleep Requirements
Understanding individual sleep needs prevents unrealistic expectations and promotes better sleep.
XII. Impact of Sleep on Overall Health
A. Holistic Health Benefits of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep supports immune function, regulates mood, and enhances cognitive performance, contributing to overall well-being.
B. Connection Between Sleep and Mental Well-being
Adequate sleep plays a pivotal role in maintaining mental health, reducing the risk of conditions like anxiety and depression.
C. Sleep’s Role in Physical Health
Quality sleep is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
XIII. Conclusion
A. Recap of Sleep Hygiene Tips
By adopting a holistic approach to sleep hygiene, including consistent routines, mindfulness practices, and dietary adjustments, one can significantly improve the quality of their sleep.
B. Encouragement for Better Sleep
Embracing these tips may take time, but the benefits of improved sleep are well worth the effort. Consistency and patience are key.
C. The Journey to Improved Sleep
Remember that achieving better sleep is a journey, and small changes can make a significant impact over time.